How to Choose a Quality Berberine Supplement (Forms, Testing, and Label Red Flags)
High-trust buyer’s-guide-style piece that teaches readers exactly how to evaluate quality and avoid common pitfalls.
By Supplement Reports Team
July 14, 2025
22 min read



Quick Take:

testing and identifying red flags that signal poor quality or questionable manufacturing practices. We’ll explore the science behind different berberine formulations, decode the complex world of supplement testing and certification, examine what makes a truly transparent and trustworthy product label, and provide practical tools for evaluating manufacturers and their quality commitments.
The supplement industry’s lack of standardized regulation means that berberine products can vary dramatically in quality, purity, and potency. Some products may contain little to no active berberine, while others may be contaminated with heavy metals, microbial pathogens, or other harmful substances. Understanding how to identify high-quality products isn’t just about getting better results—it’s about protecting your health and ensuring that your investment in supplementation actually supports your wellness goals rather than potentially undermining them.
Understanding Berberine Forms: The Foundation of Bioavailability

The primary benefit of berberine HCl lies in its consistency and predictability. Unlike plant extracts, which can vary significantly in berberine content depending on growing conditions, harvest timing, and processing methods, berberine HCl provides a standardized amount of active compound in each dose. This standardization is crucial for both research purposes and practical supplementation, as it allows for precise dosing and reproducible effects.
From a bioavailability perspective, berberine HCl offers superior solubility compared to the raw alkaloid. The hydrochloride salt formation enhances the compound’s ability to dissolve in the acidic environment of the stomach, which is the first step in the absorption process. While berberine’s overall bioavailability remains relatively low regardless of form, the HCl version represents the most efficient delivery method currently available in mainstream supplements. The manufacturing process for berberine HCl also allows for better quality control and purity assurance. The chemical synthesis process can be more precisely controlled than plant extraction methods, resulting in products with fewer impurities and more consistent potency. This consistency is particularly important for individuals who rely on berberine for ongoing metabolic support and need predictable effects from their supplementation.
When evaluating berberine HCl products, look for clear labeling that specifies the exact amount of berberine per serving, not just the total weight of the berberine HCl compound. Some manufacturers may list the weight of berberine HCl, which includes the hydrochloride portion, rather than the actual berberine content. High-quality products will clearly state both the berberine HCl amount and the equivalent berberine content.
Emerging Forms and Enhanced Delivery Systems

Dihydroberberine represents one of the most promising developments in berberine supplementation. This reduced form of berberine is created through a hydrogenation process that adds hydrogen atoms to the berberine molecule, fundamentally altering its absorption characteristics. Research suggests that dihydroberberine may be absorbed more efficiently than standard berberine HCl, potentially requiring lower doses to achieve similar effects.
The theoretical advantage of dihydroberberine lies in its improved ability to cross intestinal barriers and enter systemic circulation. Once absorbed, dihydroberberine is converted back to berberine in the body, but the enhanced absorption phase means more of the active compound reaches target tissues. However, dihydroberberine supplements are typically more expensive than standard berberine HCl, and long-term research on this form is still limited compared to the extensive database of studies on berberine HCl.
Berberine phytosome technology represents another approach to enhancing bioavailability. This formulation combines berberine with phospholipids (typically from sunflower or soy lecithin) to create a complex that may be more easily absorbed by the digestive system. The phospholipid coating is designed to protect berberine from degradation in the digestive tract and facilitate its passage across intestinal membranes.
Liposomal berberine takes the phospholipid approach a step further by encapsulating berberine molecules within lipid spheres (liposomes) that can more easily cross cellular membranes. The lipid coating protects the berberine from degradation in the digestive tract and facilitates absorption through different pathways than standard berberine HCl.
Complex Formulations and Absorption Enhancers

Piperine, derived from black pepper, is one of the most common absorption enhancers found in berberine supplements. Research suggests that piperine can inhibit certain enzymes involved in drug metabolism, potentially allowing more berberine to remain active in the system for longer periods. While this approach has theoretical merit, the practical benefits in real-world supplementation scenarios are still being evaluated, and the optimal ratio of berberine to piperine hasn’t been definitively established.
Some formulations combine berberine with other natural compounds that may work synergistically to support metabolic health. Ceylon cinnamon, chromium, alpha-lipoic acid, and bitter melon extract are common additions that may complement berberine’s effects through different mechanisms. While these combinations can be convenient and potentially beneficial, they also make it more difficult to assess the individual contribution of berberine to any observed effects.
When evaluating complex formulations, consider whether you prefer a targeted berberine supplement that you can combine with other products as needed, or a comprehensive formula that addresses multiple aspects of metabolic health in a single product. Complex formulations may offer convenience but can also be more expensive and may not allow for optimal dosing of individual components.
Time-release or sustained-release berberine formulations attempt to address the compound’s short half-life by providing a more gradual release of berberine over several hours. These formulations use various technologies, such as enteric coatings or matrix tablets, to slow the release of berberine in the digestive system. While this approach has theoretical advantages, the effectiveness of different time-release technologies can vary significantly, and these products are often more expensive than standard immediate-release formulations.
Third-Party Testing: The Gold Standard for Quality Assurance

Comprehensive third-party testing for berberine supplements should include several key analyses. Potency testing verifies that the product contains the amount of berberine claimed on the label, typically with an acceptable variance of ±10%. This testing should be conducted using validated analytical methods such as High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), which can accurately quantify berberine content.
Purity testing examines the product for contaminants that could pose health risks or indicate poor manufacturing practices. This includes testing for heavy metals (lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic), microbial contaminants (bacteria, yeast, mold), and residual solvents that might remain from the extraction or manufacturing process.
Identity testing confirms that the product actually contains berberine and not some other compound. This testing typically uses techniques like infrared spectroscopy or mass spectrometry to create a unique ‘fingerprint’ for the tested material, which is then compared to reference standards for berberine.
Dissolution testing may be included for capsule or tablet formulations to ensure that the product will break down properly in the digestive system and release its contents for absorption. This testing is particularly important for time-release or enteric-coated formulations.
The frequency of testing is also important. High-quality manufacturers conduct testing on every batch of finished product, not just occasionally or only on raw materials. Look for companies that can provide recent COAs (Certificates of Analysis) for the specific lot number of the product you’re purchasing.
Understanding Certificates of Analysis (COAs)
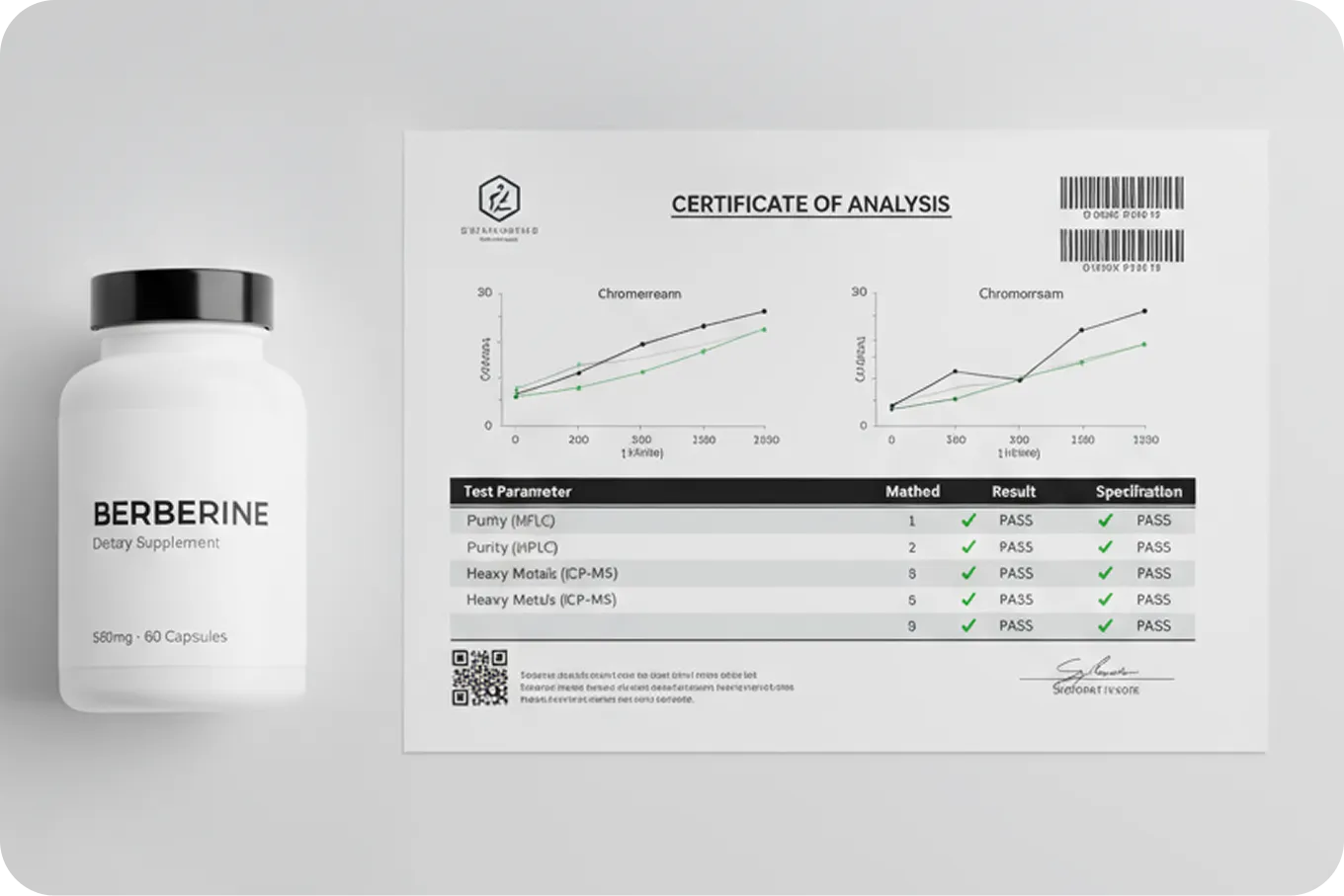
A comprehensive COA for berberine supplements should include several key sections. The identification section confirms that the tested material is indeed berberine and matches the product specifications. This typically includes results from identity testing using techniques like infrared spectroscopy or mass spectrometry, which create unique ‘fingerprints’ for different compounds.
The assay section provides quantitative results for berberine content, usually expressed as a percentage of the claimed amount. For example, if a supplement claims 500mg of berberine per capsule, the assay might show 495mg (99% of claim) or 515mg (103% of claim). Results within 90-110% of the claimed amount are generally considered acceptable.
Contaminant testing results should show levels well below established safety limits for various potential contaminants. Heavy metals should be reported in parts per million (ppm) or micrograms per gram (μg/g), with results significantly below regulatory limits. Microbial testing should show absence of pathogenic organisms and total counts within acceptable ranges.
The COA should also include information about the testing laboratory, including accreditation status and the specific methods used for each test. Look for laboratories that are ISO 17025 accredited, which indicates they meet international standards for testing competence.
Pay attention to the date of testing and the lot number or batch information. The COA should correspond to the specific product you’re purchasing, not just a representative sample from the same manufacturer. Some companies provide QR codes on their products that link directly to the relevant COA, making it easy to verify the testing results for your specific purchase.
Red Flags: Warning Signs of Poor Quality Products

Vague or misleading labeling represents one of the most common red flags in berberine supplements. Products that list ‘berberine complex’ or ‘proprietary berberine blend’ without specifying the actual berberine content should be approached with caution. Similarly, supplements that claim unrealistic berberine concentrations (such as 1000mg from a 500mg capsule) or make exaggerated health claims should raise immediate concerns.
Lack of third-party testing information is another significant red flag. While not all quality supplements prominently display testing information on their labels, reputable manufacturers should be able to provide COAs or testing results upon request. Companies that refuse to provide testing information or claim that their testing is ‘proprietary’ should be viewed skeptically.
Extremely low prices can indicate poor quality, though high prices don’t automatically guarantee quality. Berberine HCl is a relatively expensive raw material, and quality testing adds additional costs. Products that are significantly cheaper than comparable supplements may be using lower-grade raw materials, skipping quality testing, or containing less active ingredient than claimed.
Unrealistic or exaggerated marketing claims are another warning sign. Reputable supplement companies focus on providing factual information about their products and avoid making disease claims or promising unrealistic results. Be wary of products that claim to be ‘miracle cures’ or make specific medical claims about treating diseases.
Poor customer service or lack of transparency about company information can indicate broader quality issues. Reputable companies should have easily accessible contact information, knowledgeable customer service representatives, and clear policies about returns and quality guarantees.
Manufacturing Standards and Facility Certifications

Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification represents the baseline standard for supplement manufacturing in the United States. GMP facilities must follow strict protocols for cleanliness, equipment maintenance, personnel training, and quality control. However, not all GMP certifications are equal—look for facilities that specifically hold NSF International or similar third-party GMP certifications rather than self-declared compliance.
FDA registration, while not required for supplement manufacturers, indicates that a facility has voluntarily registered with the Food and Drug Administration and is subject to inspection. This registration suggests a commitment to transparency and regulatory compliance that goes beyond minimum requirements.
International certifications can provide additional quality assurance. ISO 9001 certification indicates that a manufacturer has implemented comprehensive quality management systems, while ISO 22000 focuses specifically on food safety management. These certifications require regular audits by independent organizations and demonstrate a systematic approach to quality control.
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) certification shows that a manufacturer has implemented systematic preventive approaches to food safety. This certification is particularly relevant for supplement manufacturing, as it focuses on identifying and controlling potential hazards throughout the production process.
Organic certifications, while not directly related to berberine quality (since berberine HCl is a purified compound), can indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and environmental responsibility. However, be aware that organic certification may not be applicable to all berberine forms, particularly synthetic or highly purified versions.
Sourcing and Raw Material Quality
Most commercial berberine is extracted from several plant sources, with the most common being Berberis aristata (Indian barberry), Coptis chinensis (Chinese goldthread), and various other Berberis species. The choice of source plant can influence both the quality and cost of the final product, as different species may have varying berberine concentrations and different profiles of accompanying compounds.
Geographic origin plays a crucial role in raw material quality. Plants grown in their native environments under optimal conditions typically produce higher concentrations of active compounds compared to those grown in non-native climates or under agricultural stress. Additionally, environmental factors such as soil quality, water purity, and air pollution can significantly impact the final product quality.
The timing of harvest can dramatically affect berberine content in plant materials. Berberine concentrations in plants can vary significantly depending on the season, time of day, and stage of plant development when harvesting occurs. Reputable suppliers understand these factors and time their harvests to maximize berberine content.
Processing methods used to extract berberine from plant materials can also impact quality. Traditional extraction methods may leave behind impurities or fail to extract berberine efficiently, while modern extraction techniques can produce purer, more concentrated berberine. However, harsh extraction methods might also damage the berberine or introduce unwanted chemicals.
Supply chain transparency is increasingly important in supplement sourcing. Reputable manufacturers should be able to provide information about their raw material suppliers, including details about growing conditions, harvesting practices, and initial processing methods. This transparency helps ensure that raw materials meet quality standards and are sourced ethically and sustainably.
Extraction Methods and Processing Quality
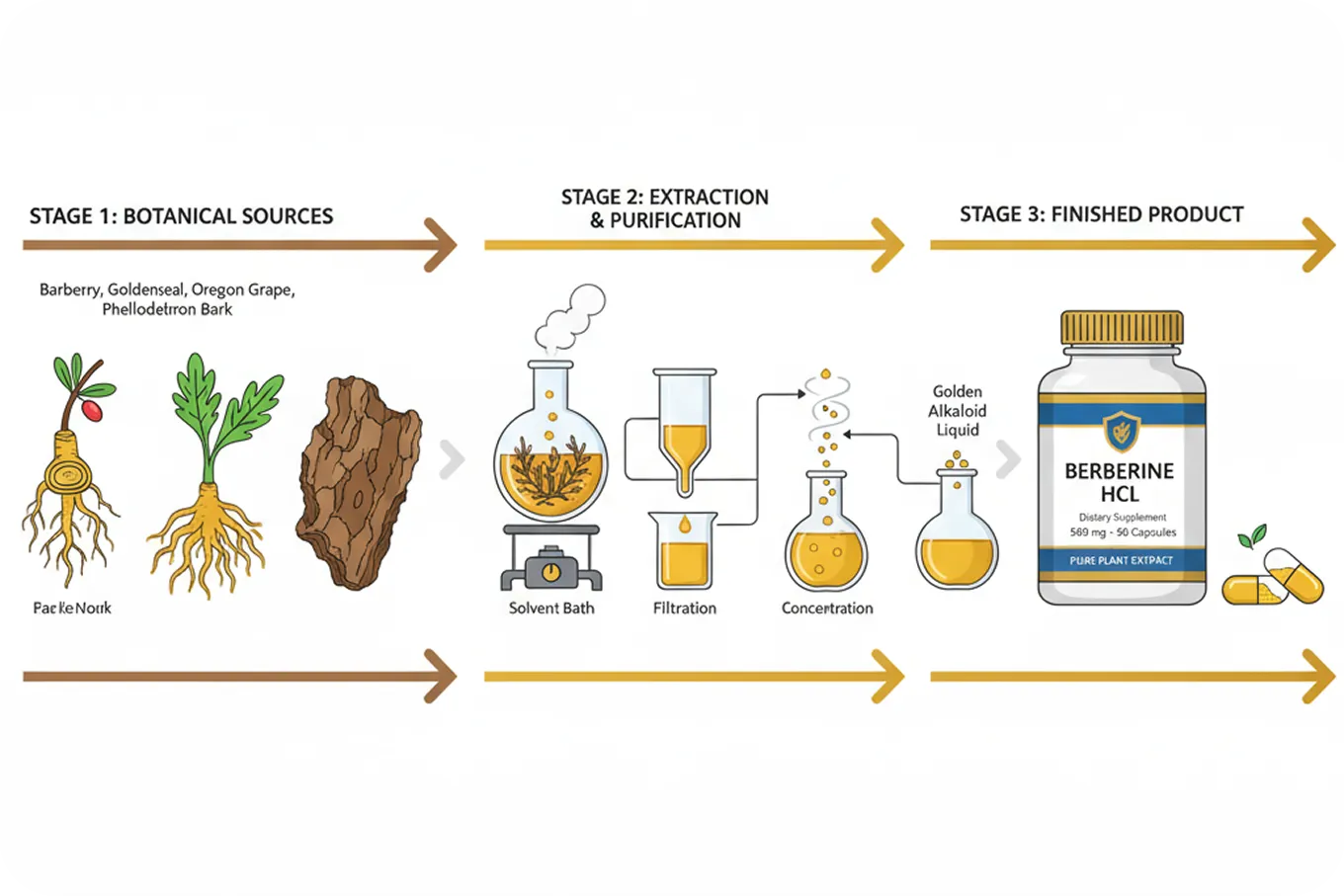
Solvent extraction represents the most common method for producing berberine supplements. This process involves using various solvents (such as ethanol, methanol, or water) to dissolve berberine from plant materials, followed by purification steps to remove unwanted compounds and concentrate the berberine. The choice of solvent and the specific extraction conditions can significantly influence the final product quality.
Ethanol extraction is generally preferred for berberine production because it effectively extracts berberine while being relatively safe and easy to remove from the final product. Ethanol is also selective for berberine and related alkaloids, helping to minimize extraction of unwanted plant compounds that might interfere with berberine’s activity or cause side effects.
Water extraction, while more natural, is less efficient for berberine extraction due to the compound’s limited water solubility. Products made using water extraction may have lower berberine concentrations and may require larger serving sizes to achieve therapeutic doses.
Supercritical CO2 extraction is a more advanced method that uses carbon dioxide under high pressure and temperature to extract berberine. This method can produce very pure extracts without leaving behind solvent residues, but it’s more expensive and may not be cost-effective for berberine production.
The purification steps following extraction are crucial for producing high-quality berberine supplements. These may include crystallization, chromatography, or other techniques to remove impurities and concentrate the berberine. The extent and sophistication of purification processes can significantly impact the final product’s purity and potency.
Quality control during processing is essential for ensuring consistent results. This includes monitoring extraction conditions, testing intermediate products, and verifying the final product’s purity and potency. Manufacturers with robust quality control systems are more likely to produce consistent, high-quality berberine supplements.
Label Literacy: Decoding Supplement Information

The Supplement Facts panel is the most important section of any supplement label, providing standardized information about serving size, ingredients, and amounts. For berberine supplements, this panel should clearly state the amount of berberine per serving, ideally specifying the form (such as ‘berberine hydrochloride’). Be wary of products that list only plant extract weights without specifying berberine content.
Ingredient lists provide additional insights into product quality and formulation philosophy. High-quality berberine supplements typically have relatively short ingredient lists, with berberine as the primary active ingredient and minimal inactive ingredients (excipients) needed for capsule formation or tablet binding. Excessive numbers of inactive ingredients, artificial colors, or unnecessary additives may indicate lower quality manufacturing or formulation practices.
Serving size information is crucial for understanding the actual berberine dose you’ll be receiving. Some products may list impressive berberine amounts but require taking multiple capsules or tablets to achieve that dose. Calculate the berberine content per individual unit to understand the practical dosing requirements.
Expiration dates and lot numbers provide important information about product freshness and traceability. Berberine can degrade over time, particularly when exposed to heat, light, or moisture. Choose products with recent manufacturing dates and store them according to label instructions to maintain potency.
Storage instructions on the label can provide insights into product stability. Berberine supplements that require refrigeration or special storage conditions may be less stable or contain additional ingredients that are sensitive to environmental conditions. While this doesn’t necessarily indicate poor quality, it does require more careful handling.
Evaluating Manufacturers and Brand Reputation
Transparency represents one of the most important indicators of a quality supplement manufacturer. Companies that readily provide detailed information about their sourcing, manufacturing processes, testing procedures, and quality control measures demonstrate confidence in their products and commitment to customer education. Look for manufacturers that provide easy access to COAs, detailed product information, and clear contact information for customer inquiries.
Scientific backing and research involvement can indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to evidence-based product development. Companies that fund or participate in clinical research, work with healthcare professionals, or employ qualified scientists and nutritionists are more likely to produce effective, well-formulated products. However, be cautious of companies that make exaggerated claims about proprietary research or use misleading scientific language to market their products.
Customer service quality can provide insights into a company’s overall professionalism and commitment to customer satisfaction. Reputable manufacturers should have knowledgeable customer service representatives who can answer detailed questions about their products, provide technical information, and handle concerns professionally. Companies that are difficult to contact or provide evasive answers to quality questions should be approached with caution.
Industry certifications and memberships can indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and professional standards. Look for companies that are members of trade organizations like the Natural Products Association (NPA) or the Council for Responsible Nutrition (CRN), which have codes of ethics and quality standards for their members.
Recall history and regulatory compliance provide important insights into a manufacturer’s quality control systems. Companies with frequent recalls or regulatory violations may have systemic quality issues. You can check the FDA’s recall database and warning letter database to research a manufacturer’s compliance history.
Longevity and stability in the market can indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. While newer companies can certainly produce high-quality products, established manufacturers with long track records may have more refined quality control systems and greater experience in supplement production.
Price vs. Quality: Finding the Sweet Spot
While price shouldn’t be the only factor in choosing berberine supplements, understanding the relationship between cost and quality can help you make value-conscious decisions without compromising on safety or effectiveness. The berberine supplement market includes products ranging from very inexpensive to premium-priced, and understanding what drives these price differences can help you identify the best value for your needs.
Raw material costs represent a significant portion of berberine supplement pricing. High-quality berberine HCl from reputable suppliers commands higher prices than lower-grade materials or crude plant extracts. Additionally, organic or sustainably sourced materials typically cost more than conventional alternatives, which can be reflected in the final product price.
Manufacturing and testing costs also contribute to price differences between products. Supplements produced in GMP-certified facilities with rigorous quality control measures and comprehensive third-party testing will typically cost more than those made with minimal quality oversight. However, these additional costs often translate to better product quality, consistency, and safety.
Brand positioning and marketing expenses can significantly influence supplement pricing, sometimes without corresponding improvements in product quality. Some premium-priced products may be paying for extensive marketing campaigns, fancy packaging, or brand recognition rather than superior ingredients or manufacturing. Conversely, some excellent quality products may be available at moderate prices from companies that focus on product quality rather than marketing.
Volume and packaging considerations can affect per-dose costs. Larger bottles or bulk packaging often provide better value per serving, but only if you’ll use the product before it expires. Consider your usage patterns and storage capabilities when evaluating different package sizes.
When comparing prices, calculate the cost per milligram of berberine rather than just comparing bottle prices. Products with different berberine concentrations or serving sizes can make direct price comparisons misleading. A more expensive product may actually provide better value if it contains more berberine per serving or requires fewer capsules to achieve the desired dose.
Making Your Final Decision: A Systematic Approach

Start by establishing your non-negotiable quality criteria. These might include third-party testing verification, GMP manufacturing, clear labeling of berberine content and form, and availability of COAs. Having clear minimum standards can help you quickly eliminate products that don’t meet your basic quality requirements.
Next, consider your specific needs and preferences. Do you prefer standard berberine HCl or are you interested in trying newer forms like dihydroberberine? Are you looking for a simple berberine supplement or a complex formulation with additional ingredients? Do you have any dietary restrictions or sensitivities that might influence your choice of inactive ingredients?
Create a shortlist of products that meet your criteria and compare them systematically. Look at berberine content per serving, cost per milligram of berberine, testing and quality certifications, manufacturer reputation, and customer reviews. This systematic comparison can help you identify the products that offer the best combination of quality and value for your specific needs.
Consider the practical aspects of supplementation, such as capsule size, dosing frequency, and storage requirements. A high-quality product that’s difficult to take consistently may be less effective than a slightly lower-quality product that fits better into your routine.
Read customer reviews and testimonials, but approach them critically. Look for patterns in reviews rather than focusing on individual experiences, and be wary of products with only extremely positive or extremely negative reviews, as these may be manipulated.
Finally, consider starting with a smaller quantity of your chosen product to assess your individual response before committing to larger purchases. Even high-quality supplements can have individual variation in effectiveness or tolerability, and starting small allows you to evaluate a product’s suitability for your needs without significant financial commitment.
Remember that choosing a quality berberine supplement is an investment in your health, and the cheapest option is rarely the best value if it doesn’t provide the intended benefits or, worse, poses safety risks. By taking a systematic approach to product evaluation and prioritizing quality indicators over marketing claims, you can identify berberine supplements that will support your health goals effectively and safely.
Disclaimer:
Top Rated Berberine Supplement
Berberine + Ceylon Cinnamon (1400mg formula)
9.8

- 1200 mg berberine equals 24,000 mg raw powder strength.
- Enhanced with Ceylon cinnamon extract for antioxidant and wellness support.
- Absorption boosted by MCT oil, Alpha-GPC, phosphatidylcholine blend.
- Promotes steady energy, focus, clarity without caffeine or stimulants.
- Manufactured in USA, purity tested, GMP-certified quality supplement.
Show more
- 1200 mg berberine equals 24,000 mg raw powder strength.
- Enhanced with Ceylon cinnamon extract for antioxidant and wellness support.
- Absorption boosted by MCT oil, Alpha-GPC, phosphatidylcholine blend.
- Promotes steady energy, focus, clarity without caffeine or stimulants.
- Manufactured in USA, purity tested, GMP-certified quality supplement.
Picked by ... people today
